-40%
Rare big Arthropleura herbivorous coprolite full plant remains not Mazon Creek !
$ 20.06
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
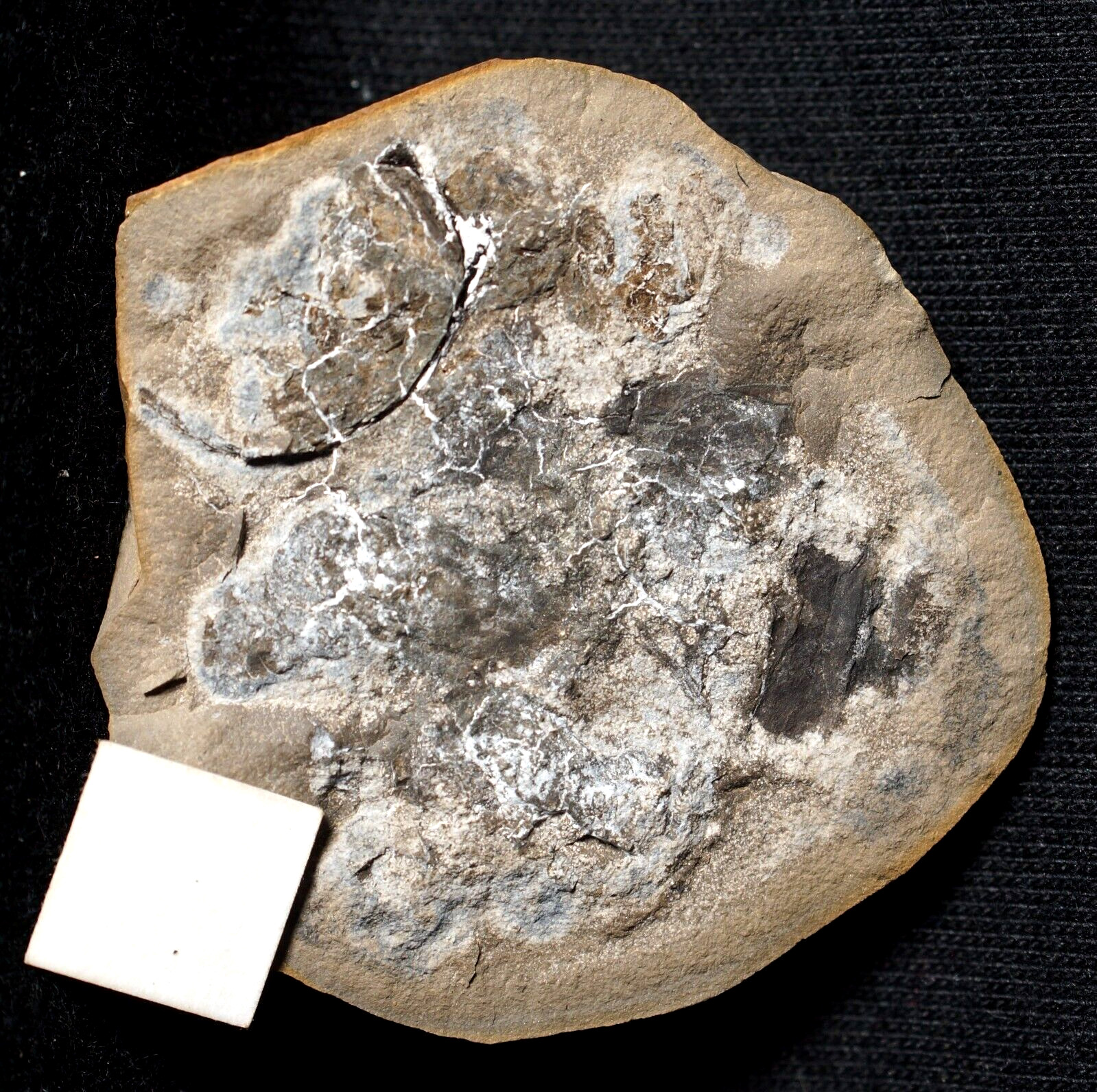
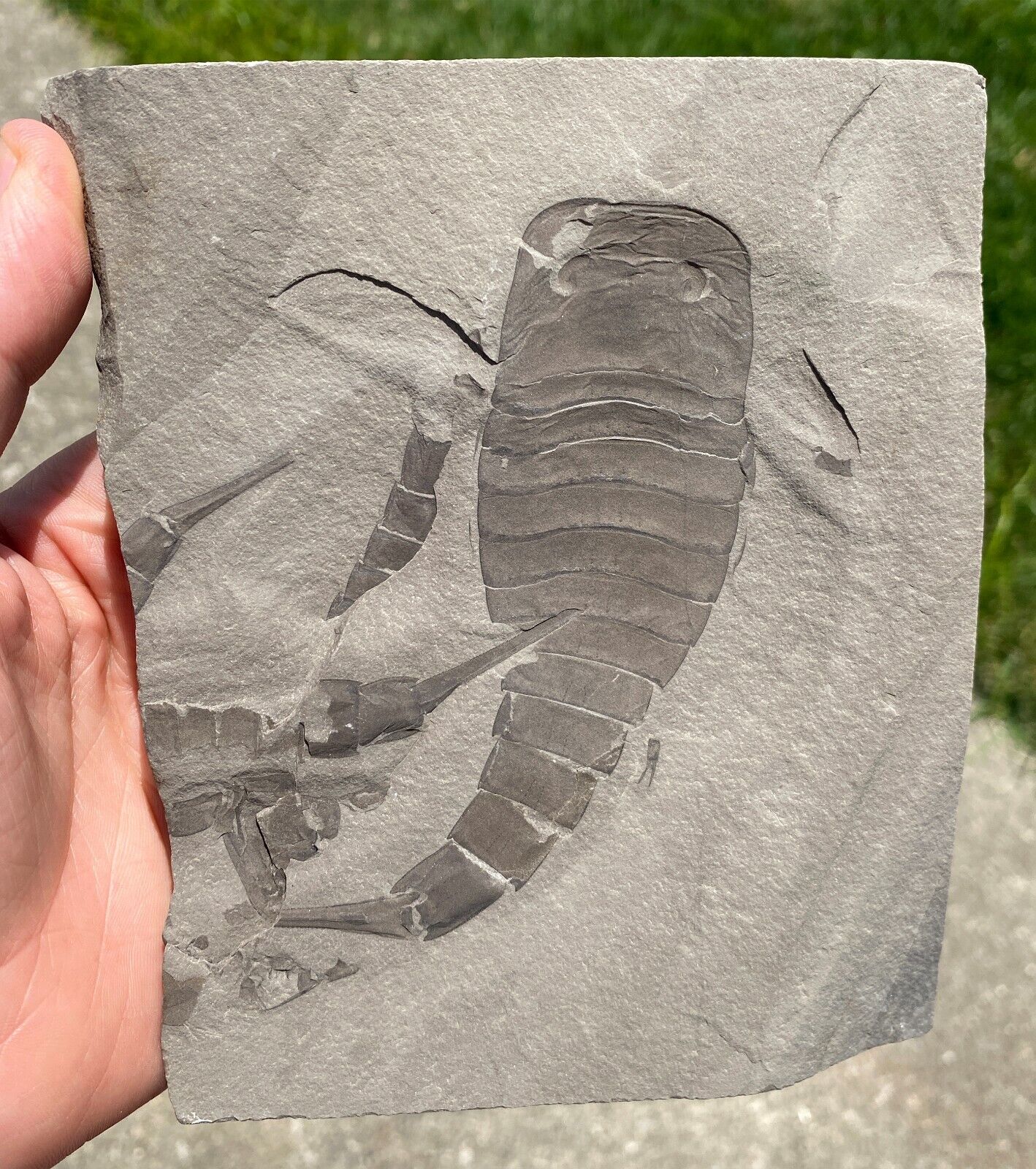
Very Rare, big , siderite nodule half with Carboniferous Arthropleura herbivorous coprolite full of plants remains , , twigs etc . Explore the Arthroplura diet !Nodule from Europe , not Mazon Creek
from closed site in Poland ! Please look pictures !
Upper Carboniferous , Westphalian A, ca. 314 mya - Zaleze beds
Poland, Sosnowiec
Nodule dimensions: 5,0 x 4,0 x 1,5 cm
Very rare, big nodule half with Carboniferous Arthropleura - herbivorous coprolite with lycopod remains , plants megasopres , twigs etc .
Arthropleura armata
Jordan 1854
-
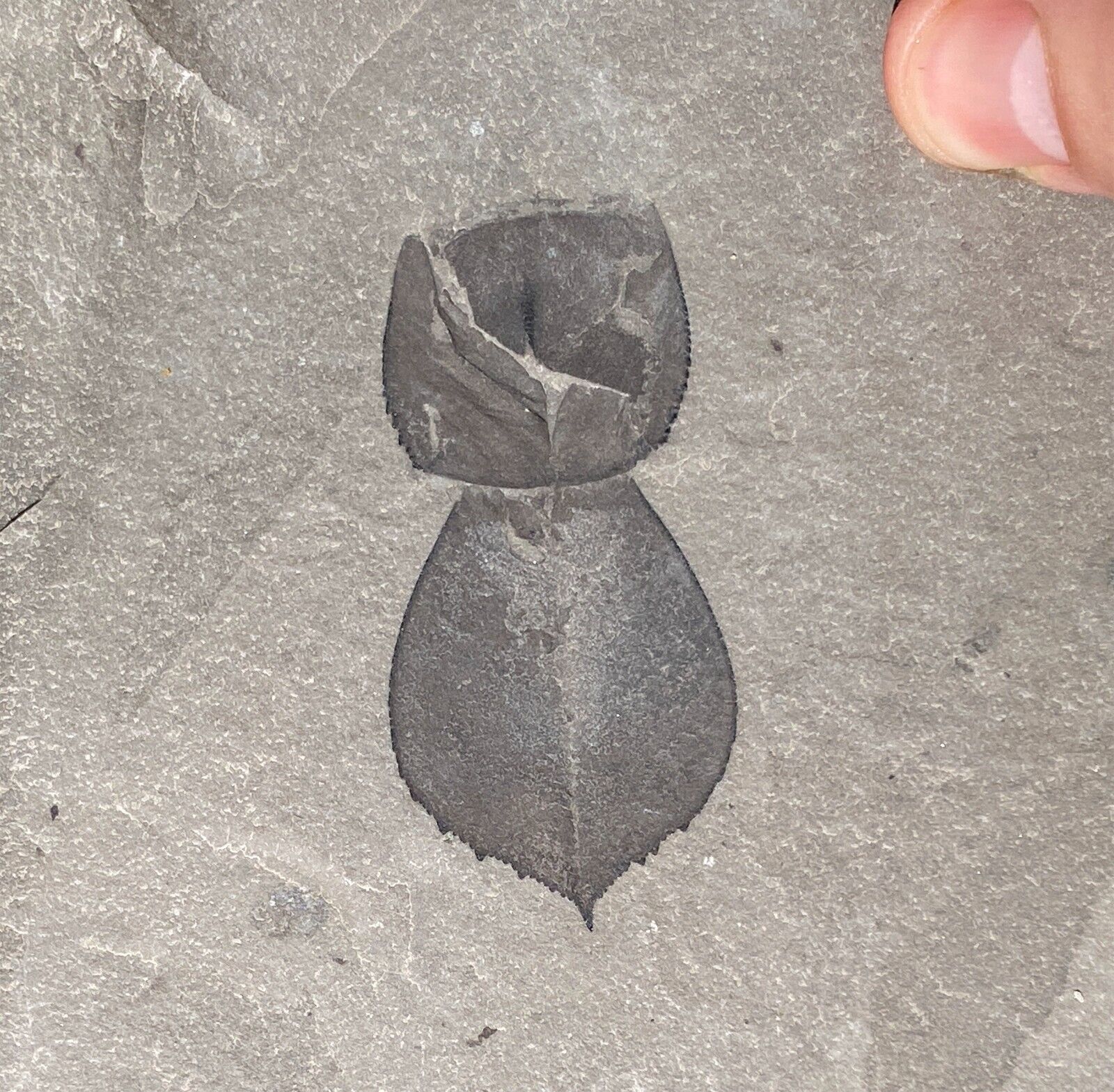
Extremely rare ,
very detailed specimen of
Arthroplura
rosette plates ! Probably respiratory organ of this giant Carboniferous millipede !
Arthropleura
specimens are found in the upper Paleozoic sediments - but only isolated armour segments in pieces. Whole specimens are extremely rare. Arthropleuridea was a class of arthropods that flourished during the Carboniferous period. Members are defined by diplosomy, paranotal tergal lobes separated from the axis by a suture, and by sclerotized plates buttressing the leg insertions. Despite their unique features, recent phylogenetic research suggests that Arthropleuridea may be included among millipedes.
The class contains three recognized orders, each with a single genus. Arthropleurids had about 30 pairs of legs, whose tracks have been found in the Joggins deposit in Nova Scotia, Canada. Arthropleuridea is most famous for order Arthropleurida. With the genus
Arthropleura
over 2 meters in length, arthropleurids are among the largest arthropods ever to have lived. The lack of large terrestrial vertebrate predators and the highly oxygenic atmosphere at that time probably enabled them to grow so large. Arthropleurids lived in the moist coal swamps that were common at the time and may have burrowed in the undergrowth. They were either herbivores or detritivores. Besides their size, their most distinguishing features were their legs with eight segments (as many as 30 pairs) and extremely tough exoskeletons. There is no evidence of spiracles, so the animals must have used lungs or gills for respiration. Arthropleurids became extinct as the climate became drier and the coal swamps dried out. Tracks from
Arthropleura
up to 50 cm wide have been found at Joggins, Nova Scotia. Most arthropleurids are thought to have been terrestrial, although, without any known respiratory structure, terrestriality is assumed only by analogy to modern arthropods. Early forms, however, including order Eoarthropleurida, appear to have been aquatic. For this reason, some question Arthropleuridea's inclusion among millipedes because no modern aquatic myriapods are known. Eoarthropleurida has been found from the Upper Silurian through the Upper Devonian of Europe and North America.
Systematic:
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Arthropoda
Subphylum: Myriapoda
Class: Arthropleuridea
Order: Arthropleurida
Family: Arthropleuridae
Genus:
Arthropleura
Species:
Arthropleura
armata
Jordan 1854